600 K Al2O3 C2H5OH [A] slope -4.00×10^(-5) mol/L•s
The decomposition of ethanol (C2H5OH) on an alumina (Al2O3) surface,
C2H5OH(g) → C2H4(g) + H2O(g) was studied at 600 K.
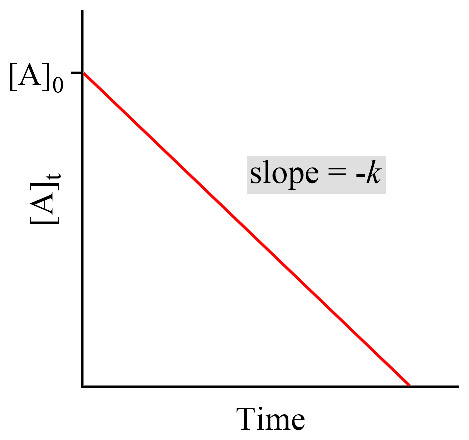
Concentration versus time data were collected for this reaction,
and a plot of [A] versus time resulted in a straight line
with a slope value of –4.00×10^(-5) mol L^-1 s^-1.
a. Determine the rate law, the integrated rate law,
and the value of the rate constant for this reaction.
b. If the initial concentration of C2H5OH was 1.25×10^(-2) M,
calculate the half-life for this reaction.
c. How much time is required for
all of the 1.25×10^(-2) C2H5OH to decompose?
600 K에서 알루미나(Al2O3) 표면에서
에탄올(C2H5OH)의 분해 반응을 조사하였다.
C2H5OH(g) → C2H4(g) + H2O(g)
이 반응의 시간에 따른 농도 변화의 실험 결과로부터
시간에 대한 [A]를 도시한 결과 직선이 얻어졌으며,
그 기울기는 –4.00×10^(-5) mol/L•s로 나타났다.
a. 이 반응에 대한 속도 법칙과 적분 속도 법칙을 써라.
그리고 이 반응의 속도 상수 값을 구하라.
b. C2H5OH의 처음 농도가 1.25×10^(-2) M이었을 때,
이 반응의 반감기를 계산하라.
c. 1.25×10^(-2) M의 C2H5OH가 모두 분해하는 데
걸리는 시간은 얼마인가?
---------------------------------------------------
a. Determine the rate law, the integrated rate law,
and the value of the rate constant for this reaction.
a plot of [A] versus time resulted in a straight line
---> 0차 반응 (zero-order)
( 참고 https://ywpop.tistory.com/6434 )
[참고] 고체 촉매 표면에서의 기체의 분해반응은
대표적인 0차 반응.
the rate law
rate = k
the integrated rate law
[A]_t – [A]_0 = –kt
the rate constant = –slope value
= 4.00×10^(-5) mol/L•s
b. If the initial concentration of C2H5OH was 1.25×10^(-2) M,
calculate the half-life for this reaction.
1.25×10^(-2) M = 0.0125 M
[A]_t – [A]_0 = –kt
[A]_0 가 ([A]_0 / 2) 될 때 시간이 반감기이므로,
t = –([A]_t – [A]_0) / k
= –((0.0125 / 2) – 0.0125) / (4.00×10^(-5))
= 156.25 s
= 156 s
c. How much time is required for
all of the 1.25×10^(-2) C2H5OH to decompose?
t = –([A]_t – [A]_0) / k
= –(0 – 0.0125) / (4.00×10^(-5))
= 312.5 s
= 313 s
[키워드] 0차 반응 기준, 영차 반응 기준, 0차 반응 사전, 영차 반응 사전

YOU MIGHT LIKE
모두 보기댓글 쓰기