aA → bB [A]_0 = 2.80×10^(-3) M +3.60×10^(-2) L/mol.s
A certain reaction has the following general form:
aA → bB
At a particular temperature and [A]_0 = 2.80×10^(-3) M,
concentration versus time data were collected for this reaction,
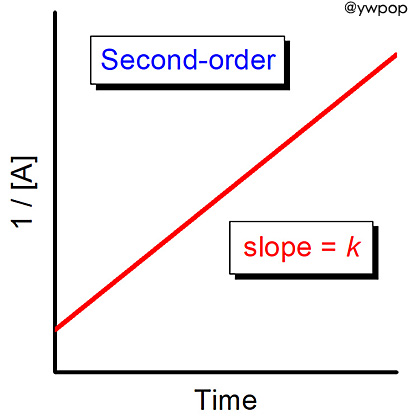
and a plot of 1/[A] versus time resulted in a straight line
with a slope value of +3.60×10^(-2) L/mol•s.
a. Determine the rate law, the integrated rate law,
and the value of the rate constant for this reaction.
b. Calculate the half-life for this reaction.
c. How much time is required for the concentration of A
to decrease to 7.00×10^(-4) M?
---------------------------------------------------
[참고] 2차 반응
[ https://ywpop.tistory.com/25 ]
a. Determine the rate law, the integrated rate law,
and the value of the rate constant for this reaction.
slope value = +3.60×10^(-2) L/mol•s
= value of the rate constant
기울기 = 속도 상수 이고,
속도 상수의 단위 = L/mol•s 이므로,
---> 2차 반응.
b. Calculate the half-life for this reaction.
2차 반응의 반감기
t_1/2 = 1 / (k [A]_0)
= 1 / [(+3.60×10^(-2) /M•s) × (2.80×10^(-3) M)]
= 1 / [(3.60×10^(-2)) × (2.80×10^(-3))]
= 9920.6 s
= 9.92×10^3 s
c. How much time is required for the concentration of A
to decrease to 7.00×10^(-4) M?
2차 반응 속도식
(1 / C_t) = k•t + (1 / C_0)
t = [(1 / C_t) – (1 / C_0)] / k
= [(1 / (7.00×10^(-4))) – (1 / (2.80×10^(-3)))] / (3.60×10^(-2))
= 29761.9 s
= 2.98×10^4 s
[키워드] 2차 반응 기준, second-order reaction graph

YOU MIGHT LIKE
모두 보기댓글 쓰기